X-RAY Origin
X-ray was first discovered on November 8, 1895 by German scientist Roentgen (W. C. Röntgen, 1845-1923).

X-ray was first discovered on November 8, 1895 by German scientist Roentgen (W. C. Röntgen, 1845-1923).
the flow of energy released from unstable atoms or atomic nuclei
[radiation of legal terms]

Radiation is defined by Presidential Decree as having the ability to direct or indirect ionize air, either electromagnetic or corpuscular beam.
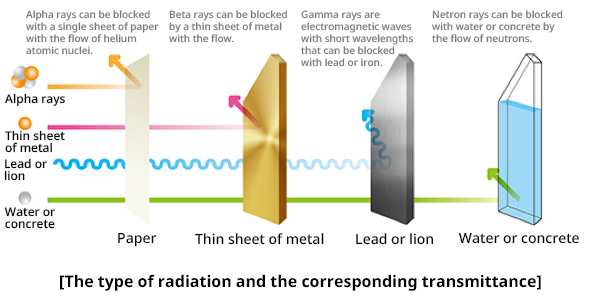
1. Alpha, deuteron, positive, beta, and other Heavy Charged Particles rays
2. Neutron rays
3. Gamma and X-ray
4. Electron rays with more than 50,000 electron volts

Natural radiation refers to the radiation of natural radioactive materials present in the natural world.
The radiation that has been on Earth since the birth of the Earth, which exists everywhere, and the average annual natural radiation dose of the world is 2.4 mSv per person, and the average of Korea is 3.08 mSv.
Artificial radiation refers to all artificially created radiation and is typical of medical and industrial x-rays.
| classification | new unit | existing unit | conversion unit | explanation | |
| radioactivity unit | Bq | Ci | 1Ci = 3.7 X 1010 Bq | It means that one atom collapses in one second. | |
| radiation unit |
Exposure Dose | C/kg | R | 1R = 2.58 X 10-4 C/kg | Charge generated per air unit mass by x-ray or r-ray |
| absorbed dose | Gy | rad | 1Gy = 100rad | energy of absorbed radiation per unit mass of material | |
| Equivalent Dose | Sv | rem | 1Sv = 100rem | The amount of absorbed dose multiplied by the weight of the corresponding radiation when representing the exposed dose of the human body. | |
| Effective Dose | Sv | rem | 1Sv = 100rem | If several tissues of the body are irradiated uniformly or unevenly in radiation, the amount to be used to assess the overall effect by reflecting the difference in relative risk by tissue, multiplied by tissue weight, is the sum of the equivalent dose of tissue or organ. | |
| radioactivity unit | Bq | |
| radiation unit | Exposure Dose | C/kg |
| absorbed dose | Gy | |
| Equivalent Dose | Sv | |
| Effective Dose | Sv | |
| radioactivity unit | Ci | |
| radiation unit | Exposure Dose | R |
| absorbed dose | rad | |
| Equivalent Dose | rem | |
| Effective Dose | rem | |
| radioactivity unit | 1Ci = 3.7 X 1010 Bq | |
| radiation unit | Exposure Dose | 1R = 2.58 X 10-4 C/kg |
| absorbed dose | 1Gy = 100rad | |
| Equivalent Dose | 1Sv = 100rem | |
| Effective Dose | 1Sv = 100rem | |